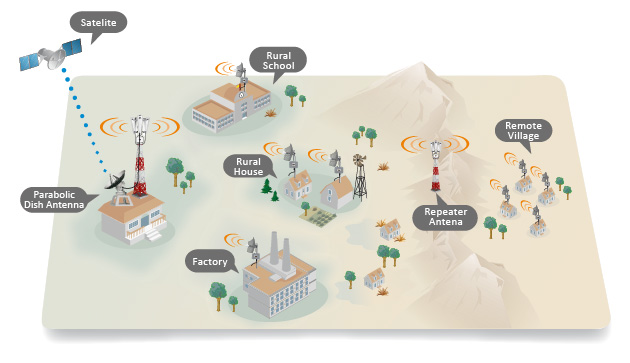
Voice telephony has been the main option for providing access to telecommunications in rural areas. Today, a wide variety of new applications such as e-mail, e-commerce, tele-education, tele-health, and tele-medicine, among others, has made access to interactive multimedia services as important as - maybe even more important than - voice connectivity alone. Since each rural district or community requires a different mix of voice, text, image, video and audio communications to best meet its needs, telecommunication network operators must be able to support the widest possible range of services and/or applications and different bandwidth levels at a reasonable cost. The Internet (with the unavailability of IP network in rural area) is the most widely used platform used to deliver multimedia applications in rural areas of developing countries.
Implementation and operation is possible at a low cost in areas where population density is low.
The system can be easily installed, even in remote and inaccessible locations.
System operation and maintenance may be carried out even where qualified technical personnel are scarce.
Implementation is possible even when basic infrastructure such as mains: electricity, running water, paved road networks, etc., are absent.